Renting an apartment can be an exciting adventure, but it often comes with the challenge of meeting the infamous ‘3 Times the Rent’ rule. So, what exactly does it mean to have 3 times the rent of $1,300? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive into the nitty-gritty of understanding, calculating, and navigating the world of income-to-rent ratios. Get ready to unlock the secrets of securing the perfect rental with ease and confidence!
Key Takeaways
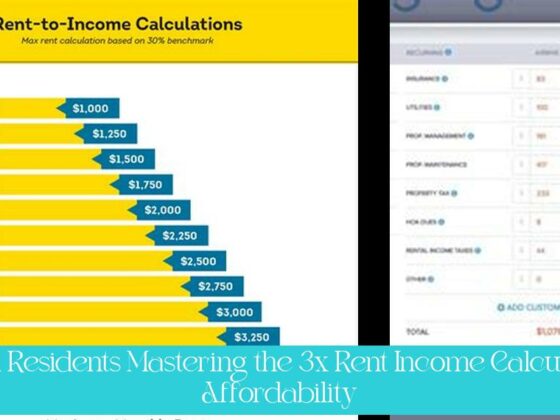
- To calculate 3 times the rent, simply multiply the monthly rent by 3. For example, if the rent is $500 per month, the income should be at least $1,500 per month.
- Mortgage lenders and private landlords often require tenants’ annual salaries to be at least three times the monthly rent.
- The best way to demonstrate 3 times the income is by providing documentation of income and savings, such as pay stubs or bank statements.
- Financial planners advise that rent should not exceed 30% of before-tax income, meaning if you earn $5,000 per month before taxes, your rent shouldn’t exceed $1,500.
- Apartment communities typically look for an annual income that is 40 times the monthly rent to determine the maximum affordable rent.
- The 3 times rent rule is based on gross income, not net income, and is used to calculate the maximum affordable rent based on income.
Understanding the “3 Times the Rent” Rule
The “3 times the rent” rule is a common requirement set by mortgage lenders and private landlords to determine if a potential tenant can afford a rental property. According to this rule, a tenant’s monthly income should be at least three times the monthly rent. This helps ensure that the tenant has sufficient financial resources to cover their rent and other living expenses comfortably.
Why is the “3 Times the Rent” Rule Important?
Mortgage lenders use the “3 times the rent” rule to assess a borrower’s ability to repay a mortgage. A higher income-to-rent ratio indicates a lower risk of default, as the borrower has a larger financial cushion to cover unexpected expenses or fluctuations in income. Similarly, private landlords use this rule to screen potential tenants and minimize the risk of late or missed rent payments.
How to Calculate 3 Times the Rent
Calculating 3 times the rent is straightforward. Simply multiply the monthly rent by 3. For instance, if the monthly rent is $1,300, the tenant’s monthly income should be at least $1,300 x 3 = $3,900. This calculation assumes that the income used is the gross income before taxes and other deductions.
Exceptions to the “3 Times the Rent” Rule
While the “3 times the rent” rule is a widely accepted standard, there may be exceptions in certain circumstances. Some landlords may consider tenants with a lower income-to-rent ratio if they have a strong rental history, a stable job, or substantial savings. Additionally, financial planners recommend that rent should not exceed 30% of a person’s before-tax income. This means that if a person earns $5,000 per month before taxes, their rent should not exceed $1,500.
Demonstrating 3 Times the Income
To prove that you meet the “3 times the rent” requirement, you can provide documentation of your income and savings. This can include pay stubs, bank statements, or tax returns. If you do not meet the income requirement on your own, you may be able to combine incomes with a roommate or co-signer.
Acceptable Forms of Income Verification
- Pay stubs: These documents provide evidence of your regular income from employment.
- Bank statements: These statements show your account activity, including deposits, withdrawals, and available balances.
- Tax returns: Your tax returns provide a comprehensive overview of your income and financial situation.
Additional Tips for Documenting Income
- Provide multiple months of documentation: This helps demonstrate consistency in your income.
- Highlight any additional income sources: This could include income from investments, self-employment, or government benefits.
- Explain any gaps in employment: If you have any gaps in your employment history, be prepared to provide an explanation.
Renting with a Lower Income-to-Rent Ratio
If you do not meet the “3 times the rent” requirement, there are still options available to you. You can consider:
— Mastering the 3x Rent Income Calculator: A Complete Guide for Affordability
Negotiating with the Landlord
Some landlords may be willing to make exceptions for tenants with a lower income-to-rent ratio, especially if you have a strong rental history or other compensating factors.
Finding a Roommate or Co-Signer
Combining incomes with a roommate or co-signer can help you meet the income requirement and increase your chances of securing a rental property.
Exploring Rental Assistance Programs
There are government and non-profit organizations that offer rental assistance programs to low-income individuals and families. These programs can help with rent payments or provide subsidies for housing costs.
Remember, finding a rental property that meets your budget and needs can take time and effort. Be prepared to research different options, negotiate with landlords, and provide documentation to support your application.
Article populaire > State Farm Dock Insurance: Comprehensive Coverage for Your Waterfront Property
How do you Calculate 3 times rent?
Calculating the 3 times rent is pretty straightforward. You simply multiply the monthly rent by 3. For example, if the rent is $500 per month, you would need to earn at least $1,500 per month (500 x 3) according to the rule.
Do you really need to make 3 times the rent?
Mortgage lenders have adopted it as a qualification ratio when approving you for a loan, and private landlords often require tenants’ annual salaries to be at least three times the monthly rent.
How do I get around 3x rent? How do you demonstrate 3x income?
The best way to demonstrate that you meet the “3 times the rent” requirement is by providing documentation of your income and savings, such as pay stubs or bank statements.