Are you ready to crack the code on the 2.5 times the rent rule? Whether you’re a renter trying to figure out if you meet the income requirements or a landlord setting guidelines for potential tenants, understanding this calculation is crucial. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll unravel the mystery behind the 2.5 times the rent rule, provide tips for both renters and landlords, and explore the factors that affect affordability. So, grab your calculator and get ready to master the art of rent calculations!
Key Takeaways
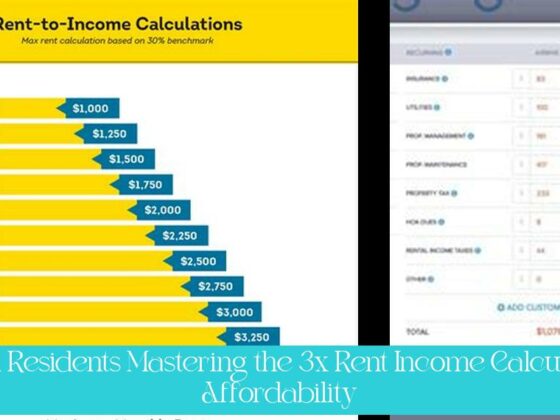
- To calculate 2.5 times the rent, simply multiply the monthly rent amount by 2.5. For example, if the monthly rent is $1,000, 2.5 times the rent would be $2,500, which is the minimum gross income required.
- For a quick estimate of how much rent you can afford, multiply your salary by 0.65 to get the after-tax income, then divide by 12 to find the monthly amount. A rule of thumb is to aim for 1/3 of your salary or less on rent.
- Landlords often require tenants to earn 2 or 3 times the amount of rent to get approved for a lease. For example, if the rent is $1,500, you would need to show $3,000 or more in monthly income as proof to qualify.
- There are various rent calculators available online to help determine the affordable monthly rent based on income and debt. These calculators consider factors such as the 40x / 30% rule to estimate rent affordability.
- When using a rent to income ratio calculator for landlords, the multiplier used, such as 2.5 or 3 times the monthly rent, determines the minimum income required for potential tenants.
- It’s important to consider the 2.5 times the rent rule when budgeting for housing, as it helps ensure that housing payments are less than 1/3 of your income, providing a guideline for financial stability.
2.5 Times the Rent Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide for Renters and Landlords

Understanding the 2.5 Times the Rent Rule
The 2.5 times the rent rule is a common standard used by landlords to determine whether a potential tenant has sufficient income to afford the rent. According to this rule, a tenant’s monthly gross income should be at least 2.5 times the monthly rent amount. For example, if the monthly rent is $1,000, the tenant should earn at least $2,500 per month. This rule helps ensure that tenants have enough income to cover their rent payments as well as other living expenses.
For you, Unlocking the 3x Rent Rule: Calculating Affordable Rent and Exceptions
There are several reasons why landlords use the 2.5 times the rent rule. First, it provides a buffer for landlords in case tenants experience financial difficulties or lose their job. Second, it helps landlords avoid rent defaults and evictions, which can be costly and time-consuming. Third, it ensures that tenants have a stable income and are less likely to move out frequently, which can lead to lost rental income for landlords.
Calculating 2.5 Times the Rent

Calculating 2.5 times the rent is a simple process. Simply multiply the monthly rent amount by 2.5. For example, if the monthly rent is $1,200, 2.5 times the rent would be $3,000. This means that a tenant would need to earn at least $3,000 per month to qualify for the apartment.
It’s important to note that the 2.5 times the rent rule is just a guideline. Some landlords may be willing to rent to tenants who earn slightly less than 2.5 times the rent, while others may require tenants to earn more. Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to rent to a tenant is up to the landlord.
>> Mastering the 2.5 Times Rent Calculator: Your Ultimate Guide to Affordability
Trending — The Ultimate Guide to the 2.5 Times Monthly Rent Rule in NYC: Everything You Need to Know
Factors that Affect Affordability
In addition to the 2.5 times the rent rule, there are several other factors that landlords consider when evaluating a tenant’s ability to afford the rent. These factors include:
- Debt-to-income ratio: This ratio measures the amount of debt a tenant has relative to their income. A high debt-to-income ratio can indicate that a tenant is struggling to manage their finances and may be at risk of falling behind on rent payments.
- Credit score: A credit score is a number that reflects a tenant’s creditworthiness. A low credit score can indicate that a tenant has a history of late payments or other financial problems, which can make landlords hesitant to rent to them.
- Employment history: Landlords want to see that a tenant has a stable employment history. This helps ensure that the tenant will have a steady income to cover their rent payments.
- Rental history: Landlords will often check a tenant’s rental history to see if they have a history of paying rent on time and taking care of their property. A positive rental history can increase a tenant’s chances of being approved for a lease.
Tips for Renters
If you’re a renter, there are several things you can do to improve your chances of being approved for an apartment and getting a good deal on rent. These tips include:
Discover – Mastering the 2.5 Times Monthly Rent Rule: A Renter’s Essential Guide
- Get your finances in order. Make sure you have a stable income and a good credit score. If you have any debts, work on paying them down.
- Be prepared to provide documentation. When you apply for an apartment, you will likely be asked to provide proof of income, such as pay stubs or bank statements. You may also be asked to provide a credit report and rental history.
- Be honest and upfront with the landlord. If you have any financial problems or a negative rental history, be honest with the landlord about it. Landlords are more likely to rent to tenants who are upfront about their situation.
- Be prepared to negotiate. The 2.5 times the rent rule is just a guideline. If you find an apartment that you love but can’t quite afford the rent, be prepared to negotiate with the landlord. You may be able to get a lower rent or a longer lease term.
Conclusion
The 2.5 times the rent rule is a common standard used by landlords to determine whether a potential tenant has sufficient income to afford the rent. By understanding this rule and the other factors that landlords consider when evaluating tenants, you can improve your chances of being approved for an apartment and getting a good deal on rent.
How does the 2.5 times the rent rule work?
The 2.5 times the rent rule states that a tenant’s monthly gross income should be at least 2.5 times the monthly rent amount. For instance, if the monthly rent is $1,000, the tenant should earn at least $2,500 per month.
Why do landlords use the 2.5 times the rent rule?
Landlords use this rule to ensure that tenants have enough income to cover their rent payments and other living expenses, provide a buffer for financial difficulties, avoid rent defaults and evictions, and ensure tenants have a stable income.
How do I calculate 2.5 times my rent?
To calculate 2.5 times the rent, simply multiply the monthly rent amount by 2.5. For example, if the monthly rent is $1,200, 2.5 times the rent would be $3,000.
Are landlords flexible with the 2.5 times the rent rule?
The 2.5 times the rent rule is a guideline, and some landlords may be willing to rent to tenants who earn slightly less than 2.5 times the rent, while others may require tenants to earn more. Ultimately, the decision is up to the landlord.
What factors affect a tenant’s affordability besides the 2.5 times the rent rule?
In addition to the 2.5 times the rent rule, landlords consider factors such as debt-to-income ratio, credit history, employment stability, and rental history when evaluating a tenant’s ability to afford the rent.
Why is it important to consider the 2.5 times the rent rule when budgeting for housing?
Considering the 2.5 times the rent rule when budgeting for housing is important as it helps ensure that housing payments are less than 1/3 of your income, providing a guideline for financial stability.