Are you ready to crunch some numbers and figure out if you can afford that dream apartment? Look no further than the 2 Times the Rent Calculator! Whether you’re a tenant trying to meet the income requirements or a landlord setting fair guidelines, understanding the “2 Times the Rent” rule is crucial. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive into income calculations, tips for finding affordable rent, and even explore some exceptions and alternatives to the rule. So, grab your calculator and get ready to master the art of budgeting for your next rental adventure!
Key Takeaways
- To calculate 2.5 times the rent, simply multiply the monthly rent by 2.5 to determine the minimum gross income required for approval.
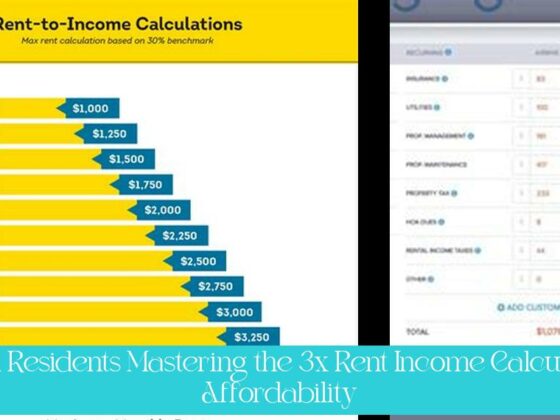
- Many places require tenants to earn 2 or 3 times the amount of rent to get approved, meaning if the rent is $1,500, the tenant would need to earn $3,000 per month.
- For a monthly rent of $2,000, 3 times the rent would require a monthly income of $6,000 to keep housing payments less than 1/3 of income.
- When considering how much rent can be afforded, a quick calculation involves multiplying the salary by .65 to determine after-tax income, then aiming for 1/3 of the salary or less on rent.
- Use rent calculators to estimate affordable monthly rent based on income and debt, and to find a rent price that fits the income, ensuring finances are in check.
- Ensure tenants can comfortably afford rent with a Rent-to-Income Ratio Calculator, considering three factors: the renter’s income, the rent amount, and the move-in date.
The 2 Times the Rent Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide for Tenants and Landlords

Navigating the rental market can be a daunting task, especially when it comes to understanding the financial requirements. One common guideline that both tenants and landlords often encounter is the “2 times the rent” rule. This rule suggests that a tenant’s monthly income should be at least twice the amount of their monthly rent. While this rule of thumb is widely used, it’s essential to dive deeper into its implications and exceptions.
Understanding the “2 Times the Rent” Rule
The “2 times the rent” rule is a general guideline used by landlords to assess a potential tenant’s ability to afford the rent. The rationale behind this rule is that it helps ensure that tenants have sufficient income to cover not only their rent but also other essential expenses such as utilities, groceries, transportation, and healthcare. By requiring tenants to earn twice the amount of rent, landlords aim to minimize the risk of rent delinquency and reduce the likelihood of tenants facing financial hardship.
— Mastering the 2.5 Times Rent Calculator: Your Ultimate Guide to Affordability
For example, if the monthly rent for an apartment is $1,500, the landlord would typically expect a potential tenant to have a monthly income of at least $3,000. This income threshold is believed to provide a reasonable buffer for tenants to comfortably cover their rent and other living expenses.
More updates: Mastering the 2.5 Times Monthly Rent Rule: A Renter’s Essential Guide
Exceptions to the “2 Times the Rent” Rule

While the “2 times the rent” rule is a common guideline, there are certain exceptions and variations that may apply in different circumstances. Some landlords may be willing to consider tenants who earn slightly less than twice the rent, especially if they have a strong rental history, a stable job, or additional sources of income.
In some competitive rental markets, landlords may be forced to relax this rule to attract and retain tenants. For instance, in areas with a high demand for housing and a limited supply of rental units, landlords may be more flexible in their income requirements to secure reliable tenants.
Alternatives to the “2 Times the Rent” Rule
In addition to the “2 times the rent” rule, there are other methods that landlords and tenants can use to assess affordability. One alternative is the “3 times the rent” rule, which requires tenants to earn three times the amount of rent. This stricter rule is often used for higher-priced rentals or in areas with a particularly competitive rental market.
Another approach is to use a rent-to-income ratio calculator. This type of calculator takes into account a tenant’s income, debt obligations, and other financial factors to determine an affordable rent range. Rent-to-income ratio calculators can provide a more personalized assessment of a tenant’s financial situation.
Calculating Your Income Needs
Trending — Mastering Affordability: Calculating 3 Times the Rent of $1,500 and Tips for Saving Money
Determining your income needs for renting an apartment is crucial for financial planning and ensuring that you can comfortably afford your rent. Here are some steps to calculate your income needs:
-
Determine Your Monthly Rent: The first step is to establish the monthly rent for the apartment you are considering. This information can be obtained from the landlord or through rental listings.
-
Multiply the Rent by 2: To calculate your income needs based on the “2 times the rent” rule, simply multiply the monthly rent by 2. This will give you the minimum gross income required for approval.
-
Consider Additional Expenses: Keep in mind that rent is not your only housing expense. You will also need to factor in utilities, parking, and other associated costs. It’s wise to estimate these additional expenses and add them to your rent when calculating your income needs.
-
Assess Your Debt-to-Income Ratio: Your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) measures the percentage of your monthly income that goes towards debt payments. Lenders typically prefer DTI ratios below 36%. Calculate your DTI by dividing your total monthly debt payments by your gross monthly income. If your DTI is high, you may need to earn more to qualify for rent.
Tips for Finding Affordable Rent
Finding affordable rent can be a challenge, but there are strategies you can employ to increase your chances of securing a rental within your budget. Here are some tips:
-
Research Different Neighborhoods: Explore different neighborhoods to compare rental prices. Consider areas that may be less popular or have a lower cost of living.
-
Negotiate with Landlords: Don’t hesitate to negotiate with landlords on the rent price. Be prepared to provide documentation of your income and financial stability to support your request.
-
Consider Roommates: Sharing an apartment with roommates can significantly reduce your rent expenses. This option is especially suitable for students, young professionals, or those who are willing to compromise on privacy.
-
Look for Rent Specials and Discounts: Some landlords offer rent specials, such as reduced rates for first-time renters or incentives for signing long-term leases. Be on the lookout for these opportunities.
Trending > Unlocking Success: Mastering the 2.5 Times Monthly Rent Rule for Landlords and Tenants
-
Explore Government Assistance Programs: If you meet certain income requirements, you may qualify for government assistance programs that provide rental subsidies or affordable housing options.
1. What is the “2 times the rent” rule?
The “2 times the rent” rule is a guideline used by landlords to assess a potential tenant’s ability to afford the rent. It suggests that a tenant’s monthly income should be at least twice the amount of their monthly rent.
2. How do I calculate 2.5 times my rent?
To calculate 2.5 times the rent, simply multiply the monthly rent by 2.5. For example, if the monthly rent is $1,000, you should multiply it by 2.5, meaning the tenant should be earning at least $2,500 per month in gross income.
3. What does 2 times the rent mean?
“2 times the rent” means that a tenant should have a monthly income of at least twice the amount of their monthly rent. For example, if the monthly rent for an apartment is $1,500, the landlord would typically expect a potential tenant to have a monthly income of at least $3,000.
4. Are there exceptions to the “2 times the rent” rule?
Yes, there are exceptions and variations to the “2 times the rent” rule. Some landlords may be willing to consider tenants who earn slightly less than twice the rent, especially if they have a strong rental history, a stable job, or additional sources of income.
5. What are some key takeaways related to the “2 times the rent” rule?
Some key takeaways include the requirement for tenants to earn 2 or 3 times the amount of rent to get approved in many places, the use of rent calculators to estimate affordable monthly rent based on income and debt, and the consideration of the Rent-to-Income Ratio when assessing affordability.
6. How does the “2 times the rent” rule benefit both tenants and landlords?
The “2 times the rent” rule benefits both tenants and landlords by ensuring that tenants have sufficient income to cover their rent and other essential expenses, minimizing the risk of rent delinquency, and reducing the likelihood of tenants facing financial hardship.